الطاقة النووية والمجتمع
By
Ilan Lipper & Jon Stone
من قبل ليبر ايلان وجون ستون
Introduction مقدمة
Only 30 years ago, nuclear energy was an
exotic, futuristic technology, the subject of experimentation and far fetched
ideas. 30 عاما فقط مضت ، كان الطاقة النووية دخيل ،
والتكنولوجيا المستقبلية ، موضوع التجريب وأفكار بعيدة المنال. Today, nuclear energy is America's second
largest source of electric power after coal. اليوم ، والطاقة النووية هي أميركا ثاني أكبر
مصدر للطاقة الكهربائية بعد الفحم. More than 110 nuclear energy plants supply
more electricity than oil, natural gas or hydropower. أكثر من 110 محطات الطاقة النووية توفير المزيد
من الكهرباء من النفط والغاز الطبيعي أو الطاقة الكهرمائية. Since 1973, they have saved American consumers
approximately $44 billion, compared to the other fuels that would have been
used to make electricity. منذ عام 1973 ، أنقذ لديهم ما يقرب من
المستهلكين الأميركيين مليار $ 44 ، مقارنة مع أنواع الوقود الأخرى التي كانت
تستخدم لتوليد الكهرباء. Since our electricity system is
interconnected, practically every American gets some electricity from nuclear
energy. لأن نظامنا الكهرباء المترابطة ، عمليا كل
أميركي يحصل على بعض الكهرباء من الطاقة النووية. In addition to the economic benefits achieved
through the use of nuclear energy, there are environmental benefits as well. وبالإضافة إلى الفوائد الاقتصادية التي تحققت من
خلال استخدام الطاقة النووية ، وهناك فوائد بيئية أيضا. There are, however, various drawbacks caused
by the production of electricity through nuclear power. هناك ، ومع ذلك ، عيوب مختلف الناجمة عن إنتاج
الكهرباء من خلال الطاقة النووية. Although there are various risks involved when
using nuclear energy as a source of power, we argue that the benefits greatly
outweigh any potential problems that may arise. على الرغم من أن هناك مخاطر المختلفة المعنية
عند استخدام الطاقة النووية كمصدر للطاقة ، ونحن نقول إن الفوائد تفوق كثيرا أي
مشاكل محتملة قد تنشأ.
Nuclear Reactors and Their Fuel Cycles المفاعلات النووية ودورات وقودهم
The use of nuclear reactors to generate
electricity continues to increase all over the world. استخدام المفاعلات النووية لتوليد الكهرباء في
تزايد مستمر في جميع أنحاء العالم. By December of 1979, about 128,000 million
watts were being generated by 249 reactors operating in 22 countries. كانون الأول / ديسمبر من عام 1979 ، ويجري
إنشاؤها واط حوالي 128000 مليون نسمة بحلول 249 مفاعلات تعمل في 22 بلدا.
Before we can truly understand how a nuclear
reactor works, we must first examine the processes that occur in its core. قبل أن نتمكن من فهم حقا كيف مفاعل نووي يعمل ، ويجب
علينا أن نفحص أولا العمليات التي تحدث في صميمها. In order for a reactor to work there needs to be
at least one free neutron per fission. من أجل مفاعل للعمل يجب أن يكون هناك واحد على الأقل
النيوترونات الحرة في الانشطار. Nuclear reactors are fueled by uranium or
plutonium in a solid form. تغذيه والمفاعلات النووية من اليورانيوم أو
البلوتونيوم في شكل صلب. They are ceramic pellets approximately the size of
the end of your finger. هم الكريات السيراميك تقريبا حجم نهاية اصبعك. These pellets are placed into 12 foot long,
vertical tubes, which are bundled together and placed underwater inside the
reactor. وتوضع هذه الكريات في 12 القدم طويلة ، الأنابيب
الرأسية ، والتي هي واحدة معا ، ووضعها تحت الماء داخل المفاعل. When the plant starts up, neutrons are let loose
to strike the uranium atoms or the plutonium atoms. عندما يبدأ المصنع بالتسجيل ، والنيوترونات وعقاله
لضرب ذرات اليورانيوم أو ذرات البلوتونيوم. When the neutrons hit either of these types of
atoms in pellets, the atoms split to release neutrons of their own, along with
heat. ضرب أي من هذه الأنواع من الذرات في الكريات ، ذرات
تقسيم النيوترونات عندما لاطلاق سراح النيوترونات خاصة بهم ، جنبا إلى جنب مع
الحرارة. On average 235U and 239Pu yield two free neutrons. 235U على متوسط العائد 239Pu واثنين من النيوترونات الحرة. Initial fissioning of 235U produces neutron
energies of 2 Mev. To convert to more everyday units, this is equal to
approximately 3.2 x 10-11J. الإنشطار الأولي من 235U تنتج طاقات النيوترونات من 2
إلكترون فولت. اليومية للتحويل إلى وحدات أكثر ، وهذا يساوي حوالي 3،2 العاشر 10 -
11J. These neutrons must be slowed down in order to increase the fission
probability in the core of the reactor. تباطأ تكون هذه النيوترونات يجب عليها من أجل زيادة
احتمال الانشطار في قلب المفاعل. The way in which these neutrons slow down is by
hitting something that has approximately its own mass. الطريقة التي تبطئ هذه النيوترونات هي ضرب شيء ما
يقرب من كتلته الخاصة. Water is effective at slowing down neutrons. Once
the neutrons slow down, they go back into Uranium and fission probability
increases considerably. المياه هي فعالة في إبطاء النيوترونات. بمجرد أن
تبطئ النيوترونات ، يعودون الى يورانيوم ويزيد من احتمال انشطار إلى حد كبير. Heat is then transferred from the core of the
reactor to the water and then induces steam. ثم نقل الحرارة هو من صميم المفاعل إلى الماء
والبخار ثم يدفع.
Sometimes a neutron and proton will combine and
produce a deuteron and therefore that neutron is now lost. Companies use heavy
water in order to alleviate this dilemma. أحيانا النيوترونات والبروتونات وسوف تجمع بين إنتاج
الديوترون ، وبالتالي أن النيوترون هي الآن فقدت. الشركات استخدام الماء الثقيل من
أجل تخفيف هذه المعضلة. Some neutrons are captured directly by 235U or
238U and gamma rays are emitted. يتم التقاط بعض النيوترونات مباشرة أو 235U 238U وأشعة غاما تنبعث. Some neutrons simply escape form the core
altogether. بعض النيوترونات الهروب ببساطة تشكل صلب تماما. These are considered fast neutrons. تعتبر هذه النيوترونات السريعة. These fast neutrons have the ability to produce a
fission reaction with 238U to produce heat and more neutrons. هذه النيوترونات السريعة لديها القدرة على إنتاج رد
فعل الانشطار مع 238U لإنتاج الحرارة والمزيد من
النيوترونات. 239U could also be produced
if 238U were to capture a slow neutron. 239U أيضا يمكن أن تنتج إذا كانت
238U لالتقاط النيوترونات البطيئة. The product rapidly decays into 239Pu. المنتج يتحلل بسرعة إلى 239Pu. 239Pu
has a greater fission probability than 235U, hence as 239Pu builds up, it
fissions and contributes fuel (neutrons) to the reactor. Control rods absorbs
neutrons in order to keep the number of neutrons, and therefore, the reactions
are controlled. 239Pu لديه أكبر من احتمال انشطار
235U ، وبالتالي 239Pu يبني ، فإنه انشطار ويساهم
الوقود (النيوترونات) للمفاعل. قضبان التحكم تمتص النيوترونات من أجل الحفاظ على
عدد من النيوترونات ، وبالتالي فهي تسيطر على ردود الفعل. They are usually made of boron steel or graphite,
since they are high neutron absorption material. جعلوا عادة من الفولاذ أو البارون الجرافيت ، لأنها
مرتفعة مواد امتصاص النيوترونات.
Pressurized Water Reactor System مفاعل نظام المياه
Pressurized
water reactors and boiling water reactors are the two major types of generators
that the US. uses to produce electricity. مفاعلات الماء المضغوط
ومفاعلات الماء المغلي هي كبرى النوعين من المولدات التي للولايات المتحدة. يستخدم
لانتاج الكهرباء. Pressurized
water reactors consist of a single fuel element assembly of up to 200 zircaloy
cadded fuel 'pins'. مفاعلات الماء المضغوط
تتكون من عنصر واحد الجمعية الوقود من zircaloy
cadded الوقود دبابيس 'ما يصل الى 200. These
'pins' are immersed in a large steel pressure vessel containing ordinary
'light' water. دبابيس 'مغمورة هذه' في
وعاء ضغط كبير من الصلب يحتوي على الماء 'الضوء' العاديين. The
light water serves as both a coolant and moderator. الماء
المبرد ضوء بمثابة وسيط على حد سواء. Light
water has a higher neutron-absorbing capacity than heavy water (D2O). ضوء
الماء له قدرة امتصاص النيوترونات أعلى من الماء الثقيل (D2O). This
causes it to increase the percentage of 235U in the core. هذا
يؤدي إلى زيادة النسبة المئوية لل235U في الصميم. Uranium
dioxide is a source of fuel for this reactor. ثاني أكسيد اليورانيوم
هو مصدر من الوقود لهذا المفاعل. The
pressure vessel consists of control rods that pass through the lid, the light
water under pressure, and the reactor core. وعاء الضغط يتكون من
قضبان التحكم التي تمر من خلال غطاء ، والماء الخفيف تحت الضغط ، وقلب المفاعل. The
water attains a temperature of approximately 270 C without boiling, due to a
pressure of about 13.8 to 17.2 MPa. الماء يبلغ درجة حرارة
270 مئوية تقريبا دون الغليان ، ونتيجة لضغط من حوالي 13،8 حتي 17،2 ميغاباسكال. This
pressure is maintained through a pressurizer. ويحتفظ هذا الضغط من
خلال الضاغط. The
'light' water passes in a closed circuit to a heat exchanger. 'الضوء'
المياه ويمر في دائرة مغلقة لمبادل حراري. This
causes the water in the heat exchanger to heat up and convert to steam. هذا
يتسبب في المياه في مبادل حراري لتسخين وتحويله إلى بخار. This
steam drives one or more turbine generators, is condensed, and pumped back to
the steam generator. هذا البخار يدفع أكثر
أو مولدات التوربينات واحد ، هو مكثف ، ويتم ضخه مرة أخرى إلى مولد البخار. Another
stream of water from a lake, river, or cooling tower, is used to condense the
steam. من
المياه من البحيرة ، أو النهر وبرج التبريد ، وتستخدم تيار آخر لتكثيف البخار. It
is necessary to shut down the reactor completely, remove the lid, and replace
an appropriate portion of the fuel pin assembly, in order to refuel it, which
occurs every 12 to 18 months. (
see above figure ) فمن الضروري لاغلاق
المفاعل تماما ، وإزالة الغطاء ، واستبدال جزء مناسب من الوقود الجمعية دبوس ، من
أجل التزود بالوقود ، والذي يحدث كل 12 إلى 18 شهرا. (انظر أعلاه الشكل)
A
potential danger exists with the possibility of a rupture of the cooling system
tubing. خطرا
محتملا مع وجود احتمال وجود تمزق في أنابيب نظام تبريد. If
this were to occur there would be no way of preventing the reactor from
overheating. Due to this danger, reactors are surrounded by a double-walled
pressure containment building and contain a number of emergency core-cooling
systems. إذا كان لهذا أن يحدث
لن يكون هناك أي وسيلة لمنع المفاعل من الانهاك ، ونتيجة لهذا الخطر ، وتحيط
المفاعلات النووية من قبل الضغط الاحتواء بناء الجدران المزدوجة وتحتوي على عدد من
أنظمة التبريد الأساسية في حالات الطوارئ.
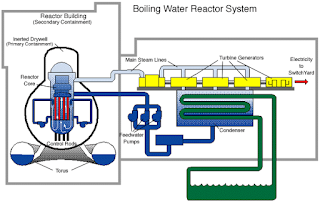
A
more efficient way of removing heat is allowing water to boil. من
الكفاءة أكثر من طريقة إزالة الحرارة هو السماح لغلي الماء. The
boiling water reactor allows the coolant within the reactor core to boil. مفاعل
الماء المغلي المبرد يسمح للداخل قلب المفاعل لتغلي. The
steam generated is then separated, dried, and passed directly to the turbine
generators. البخار الناتج ومن ثم ،
مفصولة المجففة ، ومرت مباشرة إلى مولدات التوربينات. After
going through the generators, the steam is condensed and passed back into the
reactor core. بعد أن يمر في المولدات
الكهربائية ، ويتم تكثيف البخار ومرر مرة أخرى إلى قلب المفاعل. Like
the pressurized water reactor, the boiling water reactor fuel is 235U, enriched
as uranium dioxide. مثل مفاعل الماء
المضغوط ، ومفاعل الماء المغلي الوقود 235U ، كما ثاني
أكسيد اليورانيوم المخصب. In
addition, the steam collection also occurs on top of the reactor. وبالإضافة
إلى ذلك ، وجمع البخار كما يحدث في أعلى المفاعل. One
other thing the boiling water reactor has in common with the pressurized water
reactor is that it must be shut down for refueling. ( see above figure ) شيء واحد الآخر ومفاعل
الماء المغلي في مشتركة مع مفاعل الماء المضغوط هو أن تغلق يجب أن يكون باستمرار
للتزود بالوقود. (انظر أعلاه الشكل)
As
far as safety is concerned, the entire reactor is housed within a primary
containment chamber which incorporates, underneath, a large ring-shaped tunnel
somewhat filled with water. وفيما يتعلق بالسلامة
و، يضم المفاعل هو كامل داخل غرفة الاحتواء الأولية التي تضم ، تحت ، خاتما على
شكل نفق كبير مملوء بالماء إلى حد ما. If
any water or steam were to escape, it enters this tunnel, and condenses. إن
وجدت الماء أو البخار والهرب ، فإنه يدخل هذا النفق ، ويتكثف. In
addition to this tunnel, there are several emergency systems in place. بالإضافة
إلى هذا النفق ، وهناك عدة أنظمة الطوارئ في المكان.
The Benefits of Using Nuclear Energy فوائد استخدام الطاقة النووية
Powering Our Economy: المحرك الاقتصاد لدينا :
Since
the oil embargo of 1973, Americans have used energy more wisely and more
efficiently. منذ الحظر النفطي عام
1973 ، وتستخدم الطاقة الأميركيون أكثر حكمة وأكثر كفاءة. During this time, our
population has grown from 211 million to almost 280 million, our economy has
grown about 50 percent, but our use of energy has grown only 10 percent. وخلال
هذا الوقت ، سكاننا نمت من 211 مليون إلى ما يقرب من 280 مليون دولار ، وقد نما
اقتصادنا نحو 50 في المئة ، ولكن استخدامنا للطاقة نمت 10 في المئة فقط. But our economic
growth, however, has been fueled largely by electric power. لكن
النمو الاقتصادي لدينا ، ومع ذلك ، وقد عزز إلى حد كبير من الطاقة الكهربائية.
Between
1973 and 1990, our GDP, which is the measurement of a nation's wealth, grew by
about 50 percent. In the same period, electricity use grew by 58 percent. بين
عامي 1973 و 1990 ، لدينا الناتج المحلي الإجمالي ، وهو قياس ثروة البلاد ، نما
بنحو 50 في المئة. وفي الفترة نفسها ، واستخدام الكهرباء بنسبة 58 في المئة. From this information,
we can conclude that in order to meet the needs of our strong economy and our
growing population, we must have reliable supplies of electric power. The
nation's nuclear power plants produced 674 billion kilowatt-hours of
electricity in 1996. من هذه المعلومات ،
يمكننا أن نستنتج أنه من أجل تلبية احتياجات اقتصادنا قوي وتزايد عدد السكان لدينا
، ونحن يجب أن يكون على إمدادات مضمونة من الطاقة الكهربائية. البلاد النووية
ومحطات الطاقة المنتجة 674000000000 كيلوواط / ساعة من الكهرباء في عام 1996. This was more
electricity than the entire country consumed in the early 1950s. وكان
هذا أكثر من الكهرباء المستهلكة في البلد بأكمله في أوائل 1950s. Worldwide, there are
442 nuclear power plants at work, contributing about 19 percent of the world's
electricity supply. في جميع أنحاء العالم ،
وهناك 442 محطات للطاقة النووية في العمل ، والمساهمة عن 19 في المئة من امدادات
الكهرباء في العالم.
Reduction of Dependence on Oil: الحد من الاعتماد على النفط :
At
the time of the 1973 oil embargo, oil accounted for about 17 percent of US. في
وقت الحظر النفطي عام 1973 ، شكلت النفط نحو 17 في المئة من الولايات المتحدة. electric supply;
nuclear energy was about 5 percent. 5 بالمئة ، وإمدادات
الكهرباء والطاقة النووية. In
1990, however, oil represented only about 4 percent of US electric supply,
while nuclear energy accounted for about 21 percent. Consequently, the US
imports 20 million barrels less of oil each year. For example, since l973,
nuclear energy has displaced 4.3 billion barrels of imported oil and reduced
our trade deficit by $12 billion. في عام 1990 ، ولكن
النفط لا يمثل سوى حوالي 4 في المئة من إمدادات الكهربائية الولايات المتحدة ، في
حين أن الطاقة النووية تمثل نحو 21 في المئة. وبالتالي ، فإن واردات الولايات المتحدة
20 مليون برميل من النفط أقل من كل عام ، فعلى سبيل المثال ، منذ l973 ، والمشردين
والطاقة النووية 4،3 برميل من النفط المستورد وخفض العجز التجاري مليار لدينا من
قبل 12 $ مليار. This
decrease in our trade deficit causes a direct increase of our Gross National
Product, which is also measure of a nations wealth. هذا
الانخفاض في العجز التجاري لدينا يؤدي إلى زيادة مباشرة من إجمالي الناتج القومي ،
الذي هو أيضا قدر من ثروة الأمم.
Protecting
Our Environment: حماية بيئتنا :
Nuclear
energy plants produce electricity through the fission of uranium, not the
burning of fuels. محطات الطاقة النووية
تنتج الكهرباء من خلال انشطار من اليورانيوم ، وليس حرق الوقود. Consequently, nuclear
power plants do not pollute the air with nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, dust
or greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide. وبناء على ذلك ، ومحطات
الطاقة النووية لا تلوث الهواء مع أكاسيد النيتروجين ، وأكاسيد الكبريت والغبار أو
غازات الدفيئة مثل ثاني أكسيد الكربون.
America's
nuclear energy plants reduce electric utility emissions of greenhouse gases by
20 percent, or 128 trillion tons per year. محطات الطاقة النووية
الأمريكية خفض انبعاثات الطاقة الكهربائية من الغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
بنسبة 20 في المئة ، أو 128 تريليون طن سنويا. Without our nuclear
power plants, electric utility emissions of nitrogen oxides would be 2 million
tons per year higher. Emissions of sulfur dioxide would be 5 million tons a
year higher. دون محطات الطاقة
النووية لدينا ، من انبعاثات أكاسيد فائدة النيتروجين سوف الكهربائية هو 2 مليون
طن سنويا أعلى. انبعاثات ثاني أكسيد الكبريت سيكون 5 ملايين طن في السنة أعلى من
ذلك. Thus,
nuclear energy has drastically cut our dependence on foreign imported oil. وهكذا
، بشكل جذري وخفض الطاقة النووية اعتمادنا على النفط المستورد الأجنبي.
In
France for example, from 1980 to 1986, SO2 and NOX emissions in the electric
power sector were reduced by 71% and 60% respectively, causing reductions of
56% and 9% respectively, in total SO2 and NOX emissions in France (Trudeau
160). في
فرنسا على سبيل المثال ، 1980 حتي 1986 ، وأكاسيد النيتروجين الانبعاثات في الطاقة
الكهربائية وخفض غاز SO2 والقطاع بنسبة
71 ٪ و 60 ٪ على التوالي ، مما تسبب في تخفيض 56 ٪ و 9 ٪ على التوالي ، في وغاز SO2 مجموع انبعاثات
أكاسيد النيتروجين في فرنسا (160 ترودو ).
Nuclear
energy also offers an alleviation of the global carbon dioxide (CO2) problem
that the world can do without. إن الطاقة النووية توفر
أيضا التخفيف من انبعاثات غاز ثاني أكسيد الكربون في العالم الكربون (CO2) المشكلة أن
العالم يمكن أن تفعله دون. About
1,600 million tons of CO2 annual emissions would have resulted if 16 percent of
the world's electricity now generated by nuclear power were to have been
generated using coal. طن من CO2 الانبعاثات
السنوية سوف يكون نتج عن 1600 مليون إذا كان 16 في المئة من العالم الكهرباء
المولدة من الطاقة النووية الآن قد تم إنشاؤها باستخدام الفحم. This is a significant
amount. In fact, it is 8 percent of CO2 now emitted annually from the burning
of fossil fuels. وهذا مبلغ كبير ، وفي
الحقيقة ، فإنه من 8 في المئة من CO2 المنبعثة سنويا
من الآن وحرق الوقود الاحفوري.
Another important benefit that nuclear
generated energy has on our environment is that the wastes produced are
completely isolated from the environment. فائدة أخرى المهم أن الطاقة المولدة النووي على
بيئتنا هو أن تماما عزل النفايات المنتجة من البيئة. Would we have produced the electricity with
coal instead of nuclear energy, at least 90,000 tons of toxic heavy metals
would have been released, in addition to tremendous amounts of CO2, SO2, and
NOx. سيكون لدينا إنتاج الكهرباء مع الفحم بدلا من
الطاقة النووية ، وطنا من المعادن الثقيلة السامة قد يكون على الأقل 90000 المفرج
عنهم ، بالإضافة إلى كميات هائلة من CO2 ، SO2 ، وأكاسيد النيتروجين. Some of these toxic heavy metals include
arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury. بعض المعادن الثقيلة السامة وتشمل هذه الزرنيخ
والكادميوم والرصاص والزئبق. Although the radioactive wastes produced by
nuclear energy may be dangerous for thousands of years, part of the waste
caused by the burning of coal remains dangerous forever. على الرغم من أن النفايات المشعة التي تنتجها
الطاقة النووية قد يكون خطرا لآلاف السنين ، وهو جزء من النفايات الناجمة عن حرق
الفحم تظل خطرة إلى الأبد.
The environmental benefits of nuclear energy
can he seen clearly in France. الطاقة النووية يمكن أن ينظر إليه وفوائد بيئية
واضحة في فرنسا. In the 1980s, because of concerns over imported oil, France more
than tripled its nuclear energy production. في 1980s ، بسبب القلق على النفط
المستورد ، وفرنسا أكثر من ثلاثة أضعاف في إنتاج الطاقة النووية. During that same period, total pollution from
the French electric power system dropped by 80-90 percent. خلال تلك الفترة نفسها ، من التلوث الفرنسية
أسقطت نظام الطاقة الكهربائية الإجمالي بنسبة 80-90 في المئة.
Worldwide Benefits: فوائد على مستوى العالم :
More than 400 nuclear power plants are
operating in 25 countries around the world today, supplying almost 17 percent
of the world's electricity. أكثر من 400 محطات الطاقة النووية تعمل في 25
بلدا حول العالم اليوم ، وتوفير ما يقرب من 17 في المئة من الكهرباء في العالم. In most countries, nuclear energy plays an
even larger role as a source of electricity than in the United States. في معظم البلدان ، والطاقة النووية تلعب دورا
أكبر كمصدر للكهرباء مما كانت عليه في الولايات المتحدة. Many of these nations are building new nuclear
energy plants to meet the needs of their growing populations and expanding
economies. العديد من هذه الدول على بناء محطات جديدة
للطاقة النووية لتلبية احتياجات العدد المتزايد من السكان والاقتصاديات في التوسع. About 83 new nuclear energy plants are
currently being built around the world. جديدة للطاقة النووية حاليا هي 83 عن النباتات
التي يجري بناؤها في جميع أنحاء العالم.
The Drawbacks to using Nuclear Energy عيوب لاستخدام الطاقة النووية
Despite the fact that nuclear energy offers
great benefits as an alternative source of electric power, nuclear energy as a
whole, is still a controversial issue in many countries. The reasons for this
center round the issues of safety, waste, and nuclear weapons. على الرغم من أن الطاقة النووية توفر فوائد
كبيرة كمصدر بديل للطاقة الكهربائية ، والطاقة النووية ككل ، لا تزال مسألة مثيرة
للجدل في العديد من البلدان ، وأسباب هذه الجولة مركز قضايا السلامة ، والنفايات ،
والأسلحة النووية.
Nuclear Safety الأمان النووي
National and international anxiety about nuclear
power stems directly from a fear of release of radioactive material and its consequences
on people and the environment. الوطنية والقلق الدولي حول الطاقة النووية ينبع
مباشرة من الخوف من الإفراج عن المواد المشعة وآثاره على الناس والبيئة. The problem, however, is that there is a huge
information gap between specialists on the exposures from nuclear power and the
public. المشكلة ، ومع ذلك ، هو أن هناك فجوة كبيرة بين
المعلومات المتخصصين في هذا التعرض من الطاقة النووية والجمهور. When one looks at the 1991 report by the United
Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, (UNSCEAR) one
would see that the routine generation of nuclear electricity releases only
negligible amounts of radioactive materials to the environment. عندما ينظر المرء في تقرير عام 1991 من قبل اللجنة
العلمية للأمم المتحدة المعنية بآثار الإشعاع الذري ، (اللجنة العلمية) هل للمرء
أن يرى أن الجيل روتينية من الكهرباء النووية النشرات كميات ضئيلة فقط من المواد
المشعة على البيئة. "The average dose any
individual in the world receives each year from all of the activities in the
peaceful nuclear fuel cycle is less than 0.1 percent of the inevitable
exposures he or she receives from natural radiation sources, such as cosmic
rays and radon emitting building materials" ( Trudeau 59). "إن متوسط الجرعة أي فرد في العالم يستقبل
سنويا من جميع الأنشطة في دورة الوقود النووي السلمي هو أقل من 0،1 في المئة من
التعرض لا مفر منه فانه او انها تتلقى من مصادر الإشعاع الطبيعية ، مثل الأشعة
الكونية والتي ينبعث منها غاز الرادون مواد البناء "(ترودو 59).
One has to accept that electricity production
can't be totally free of risk. على المرء أن يقبل أن إنتاج الكهرباء لا يمكن أن
تكون خالية تماما من المخاطر. The accident at Chernobyl, in the former USSR,
was undoubtedly the most severe radioactive accident the world has experienced
since the arrival of nuclear energy as an alternative source of electric power. الحادث الذي وقع في تشيرنوبيل ، في السابق ، وكان
اتحاد الجمهوريات الاشتراكية السوفياتية مما لا شك فيه حادث شديد المشعة أكثر دول
العالم قد شهدت منذ وصول الطاقة النووية كمصدر بديل للطاقة الكهربائية. Although there 31 deaths can be attributed to the
Chernobyl accident, there are many misgivings about the true nature of the
accident. وفاة يمكن أن تعزى بالرغم من وجود 31 لحادثة
تشيرنوبيل ، وهناك شكوك كثيرة حول الطبيعة الحقيقية للحادث. For example, the people who died, including the
nuclear operators and the figherfighters, received very high doses, unlike the
surrounding areas that were relatively safe from exposure to high radiation
levels. على سبيل المثال ، الناس الذين لقوا حتفهم ، بما في
ذلك النووية ، والمشغلين ، figherfighters تلقى جرعات عالية جدا ، على
عكس المناطق المحيطة بها التي كانت آمنة نسبيا من التعرض لمستويات عالية من
الإشعاع. "Contrary to some
erroneous reports, no accurate health effects from the incident have been found
in the population in the Ukraine and Byelorussia. Elsewhere in Europe,
countermeasures taken in many countries immediately after the accident
effectively reduced the levels of exposure to the public" (Trudeau 159). "خلافا لبعض التقارير الخاطئة ، وآثار الحادث
من لم يتم العثور على دقة الصحية في عدد السكان في أوكرانيا وروسيا البيضاء. وفي
أماكن أخرى في أوروبا ، والتدابير المضادة التي اتخذت في كثير من البلدان على
الفور بعد وقوع الحادث على نحو فعال خفض مستويات التعرض للجمهور" ( ترودو
159). One can also see from UNSCEAR data that outside of the Soviet
Union, the Chernobyl accident has emitted a dose that is a fraction of what the
population receives every year from natural radiation found. يمكن للمرء أن يرى أيضا أن من بيانات اللجنة
العلمية من خارج الاتحاد السوفياتي ، وحادثة تشرنوبيل والتي تنبعث جرعة هو جزء
بسيط من السكان ما يحصل كل سنة من الإشعاعات الطبيعية الموجودة.
One positive result from the tragic Chernobyl
accident is that there is now increased awareness and commitment of the nuclear
community to international cooperation in the field of safety. "Through
the efforts of utilities and governments, of the IAEA and others, an
international nuclear safety regime is emerging, which includes a wide range of
arrangements for improving operational safety and emergency preparedness and response
to accidents" (Trudeau 159). نتيجة إيجابية واحدة من حادثة تشرنوبيل المأساوية
هي أن هناك الآن زيادة الوعي والالتزام من المجتمع النووية للتعاون الدولي في مجال
السلامة. "من خلال الجهود التي تبذلها الحكومات والمرافق العامة ، من وكالة
الطاقة الذرية وغيرها ، والنظام الدولي للسلامة النووية والناشئة ، والتي تشمل
مجموعة واسعة من الترتيبات لتحسين السلامة التشغيلية والتأهب لحالات الطوارئ
والاستجابة للحوادث "(ترودو 159).
The United States has also had a serious accident
concerning the production of nuclear energy. الولايات المتحدة كان لها أيضا لحادث خطير بشأن
إنتاج الطاقة النووية. "An accident with
potential for a core meltdown occurred in the PWR at the Three Mile Island
Nuclear Station Unit 2 near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, on March 28, 1979" (
Glasstone 105). "حادث مع احتمال حدوث الأساسية وقع الانهيار
أحد في الماء المضغوط في ثري مايل ايلاند وحدة بالقرب من محطة نووية 2 هاريسبيرغ
بولاية بنسلفانيا ، في 28 مارس 1979" (Glasstone 105). The three Mile Island accident appears to have
resulted from a combination of design deficiencies, inadequate procedures, and
operator errors. ثلاثة حادث مايل ايلاند يبدو أنها نتجت عن مزيج من
عيوب التصميم ، والإجراءات غير كافية ، والأخطاء المشغل. "The
consequences will be far reaching" (Glasstone). Like the Chernobyl
accident, some good has come from the accident at Three Mile Island. "عواقب وسوف تكون بعيدة المدى" (Glasstone) ، ومثل حادث تشرنوبيل ، بعض
جيدة قد حان من الحادث الذي وقع في ثري مايل ايلاند. After the accident, the Electric Power Research
Institute established a Nuclear Safety Analysis Center to review and analyze
information relative to the safety of nuclear power plants. بعد الحادث ، ومعهد أبحاث الطاقة الكهربائية وإنشاء
مركز تحليل السلامة النووية لاستعراض وتحليل المعلومات المتعلقة سلامة محطات
الطاقة النووية. The fact of the matter is that nuclear power plants are safer today
than ever before, and they will be unquestionably safer tomorrow than today. وحقيقة الأمر أن محطات الطاقة النووية هي أكثر أمنا
اليوم من أي وقت مضى ، وأنها سوف تكون أكثر أمنا مما لا شك فيه غدا من اليوم.
Nuclear Waste النفايات النووية
Another drawback that is often associated with
the use of nuclear energy is that of nuclear waste. عيب آخر أن كثيرا ما يرتبط استخدام الطاقة النووية
هو أنه من النفايات النووية. There is a huge misunderstanding that the waste
created by nuclear energy is more "dangerous" than that of other
means of producing electricity. هناك سوء فهم ضخمة من النفايات الناجمة عن الطاقة
النووية هي أكثر "خطير" من ذلك من وسائل أخرى لتوليد الكهرباء. The truth of the matter is that radioactive waste
from nuclear energy may be dangerous for thousands of years, while wastes
resulting from the burning of coal, remains dangerous forever. حقيقة الأمر هي أن النفايات المشعة من الطاقة
النووية قد يكون خطرا لآلاف السنين ، في حين أن النفايات الناتجة عن حرق الفحم ، لا
تزال خطيرة إلى الأبد. The reason for this is because the toxicity of
these stable elements does not decrease over time as does the toxicity of
radioactive materials. والسبب في ذلك لأن هذه العناصر السمية مستقر لا
يتناقص مع مرور الوقت كما يفعل سمية المواد المشعة.
Other interesting facts concerning nuclear waste
include the reduction in emissions of SO2 and NOx in countries using nuclear
power is revealing. حقائق أخرى مثيرة للاهتمام بشأن النفايات النووية
تتضمن خفض انبعاثات غاز SO2 في وأكاسيد النيتروجين في البلدان التي تستخدم الطاقة
النووية كاشفة. "In France, for
example, during the period from 1980 to 1986, SO2 and NOX emissions in the
electric power sector were reduced by 71 percent and 60 percent, respectively,
making a major contribution to reductions of 56 percent and 9 percent,
respectively, in total SO2 and NOX emissions in France" (Trudeou p.160). "في فرنسا ، على سبيل المثال ، خلال الفترة
1980 حتي 1986 ، وأكاسيد النيتروجين الانبعاثات في الطاقة الكهربائية وخفض غاز SO2 والقطاع بنسبة 71 في المئة و
60 في المئة ، على التوالي ، مما يجعل مساهمة كبيرة في تخفيض 56 في المئة و 9 في
المئة ، على التوالي ، غاز SO2 في إجمالي انبعاثات أكاسيد
النيتروجين وفي فرنسا "(Trudeou p.160). These tremendous reductions were made possible by
a fourfold increase in nuclear electricity generation. وكانت هذه التخفيضات الهائلة بفضل زيادة أربعة
أضعاف في توليد الكهرباء النووية.
Nuclear Weapons الأسلحة النووية
A major drawback to the peaceful use of
civilian nuclear power for the production of electricity is that it has allowed
for the production of nuclear weapons. والعيب الرئيسي في الاستخدام السلمي للطاقة
النووية المدنية من أجل إنتاج الكهرباء التي سمحت له لإنتاج أسلحة نووية. While there is no question that nuclear energy
has various benefits, the fact that nations can create nuclear weapons of mass
destruction t is particularly disturbing. Atomic weapons are created through
the splitting of the atom and detonated through the process of fission, while
hydrogen bombs are detonated through the process of fusion. ولئن كان هناك شك في أن الطاقة النووية له فوائد
مختلفة ، وحقيقة أن الأمم يمكن أن تخلق من الأسلحة النووية تي الدمار الشامل يبعث
على القلق بشكل خاص. إنشاؤها هي الاسلحة النووية من خلال تقسيم الذرة وتفجيرها من
خلال عملية الانشطار ، في حين أن القنابل الهيدروجينية هي انفجرت خلال عملية
الانصهار. Hydrogen bombs are 1000 times more explosive than atomic bombs,
thus nations with hydrogen bomb technology can destroy nations within minutes. القنابل الهيدروجينية هي 1000 مرات أكثر تفجرا
من القنابل الذرية ، وبالتالي مع الأمم تكنولوجيا القنبلة الهيدروجينية يمكن أن
تدمر الأمم في غضون دقائق. This thought has led to intense debate over
the issue of nuclear energy as an alternative source for energy. وقد أدى هذا الفكر لمناقشة مكثفة حول قضية
الطاقة النووية كمصدر بديل للطاقة.
Conclusion استنتاج
Overall, nuclear energy has proven to be most
beneficial to our society. وعموما ، فقد ثبت أن الطاقة النووية الأكثر
فائدة لمجتمعنا. As a result of this technology, the United States has decreased
its dependency on foreign-imported oil. نتيجة لهذه التكنولوجيا ، والولايات المتحدة
انخفضت لديه اعتمادها على استيراد النفط الأجنبي. In fact, the United States saves about 12
billion dollars each year through the lack of oil it imports from other
nations. وفي الواقع ، فإن الولايات المتحدة يوفر حوالي
12 مليار دولار سنويا من خلال عدم وجود النفط التي تستوردها من دول أخرى. Nuclear energy has also proven to be a
protector of the environment because of the lack of CO2, greenhouse gasses, and
other gases it emits into the atmosphere. وقد ثبت أيضا الطاقة النووية ليكون حاميا للبيئة
بسبب عدم وجود CO2 ، والغازات المسببة
للاحتباس الحراري ، والغازات الأخرى التي تنبعث في الجو. There are, however, some major drawbacks to
using nuclear energy. ولكن هناك بعض العوائق الرئيسية لاستخدام الطاقة
النووية. These drawbacks include the actual safety of using nuclear
energy, the waste it produces, and the atomic weapons that nuclear energy
promotes. وتشمل هذه العوائق الفعلية من سلامة استخدام
الطاقة النووية ، والنفايات التي تنتجها ، والأسلحة الذرية أن الطاقة النووية
يعزز. Overall, however, we believe that the use of nuclear energy
greatly outweighs any other source of energy. وعموما ، ومع ذلك ، فإننا نعتقد أن استخدام
الطاقة النووية تفوق بدرجة كبيرة اي مصدر آخر للطاقة.
بإشراف المعلمة :خديجة الكعتلي
عمل الطالبتان:نوف والهنوف الزيادي
الفصل:2 :4